Fall Capstone Final Presentation Schedule and Information
AI Guide Dog: Predicting Egocentric Movement on a Smartphone
Abhishree Shetty, Aishwarya Jadhav, Jeffery Cao, Aditi Sharma, Ben Sukboontip, Jayant Sravan Tamarapalli, Jingyi Zhang, Urvashi Priyam Kumar AI Guide Dog attempts to democratize egocentric trajectory prediction on a smartphone for the blind community. We propose an end-to-end data pipeline for self-supervised egocentric trajectory prediction research consisting of the following: (1) a data collection module ingesting data signals generally accessible through default sensors and software stack that ship with popular smartphones; (2) a data annotation module built on top of collected data that requires minimal human tuning: (3) an egocentric modeling module to provide future directions to the users.We also demo an iOS application that takes advantage of the learned models to make real-time predictions. We will release our dataset and models post-publication. |
Komatsu: Intelligent Longwalls
Anveshrithaa Sundareswaran, Ge Huang, Zhiyi Li, Zhouyang Li Komatsu is a leading manufacturer of mining equipment. Komatsu uses intelligent longwall systems that capture machine data from automated, connected machinery and transform it into useful decision-making knowledge to support decision-making in machine operation and maintenance. This project aims to apply machine learning to build and deploy pipelines for identifying correlations, patterns, and anomalies in longwall machines to improve the operational efficiency of the machines and reduce energy consumption. |
SimBot - Navigation and Interaction
Adhokshaja Madhwaraj, Jessica Zhong, Kushagra Mahajan, Malaika Vijay, Sai Vishwas Padigi, Vineeth Reddy Vatti Embodied task-completion agents are intelligent agents that can perceive, navigate, and manipulate objects in an environment. We developed a bot for the SimBot challenge in conversational embodied task completion, where users can converse with and guide the bot to complete tasks in a 3D environment. The Navigation and Interaction thrust of the SimBot project focuses on scene understanding and action planning to perform actions that satisfy a user’s instruction. Our primary contributions include an Image Segmentation model to identify objects of interest and an Action Planning module capable of generating a logical sequence of actions to execute on the simulator. |
SimBot Dataset Collection: An Embodied Vision-Audio-Navigation Task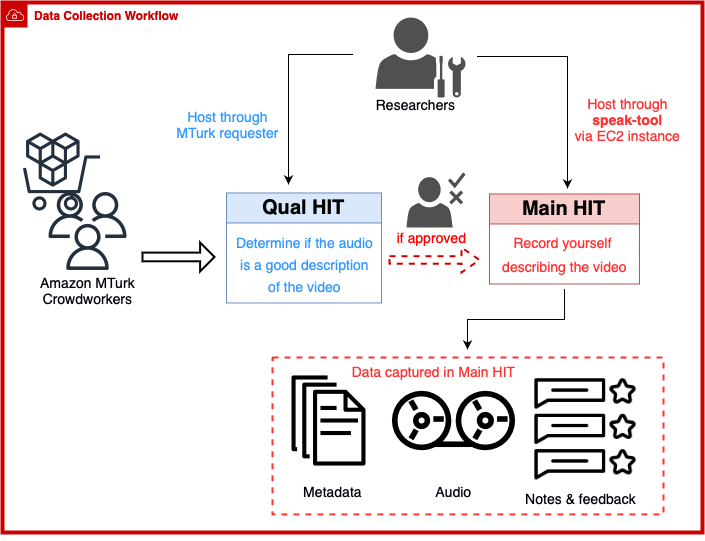
Bharani Ujjaini Kempaiah, Linyi Li Intelligent robotic agents that operate in human spaces must be capable of realizing and executing instructions that are conveyed in natural language via speech. Most existing vision and language benchmarks contain instructions in natural language via text, and subsequently, models trained on these datasets also rely heavily on text as an intermediate medium to achieve grounding. In this work, we aim to enhance the existing ALFRED benchmark by crowd-sourcing speech annotations for existing ALFRED demonstrations of household tasks. We build web interfaces to qualify crowd workers before collecting speech annotations online. With these speech annotations, we believe the research community can develop models that can power robots to achieve audio-visual grounding similar to how humans interact in the real world. |
Learn-to-Race: A Multimodal Control Environment for Autonomous Racing
Kevin Chian, Arav Agarwal, Sidharth Kathpal, Yujun Qin, Tanay Gangey Autonomous racing is a sub-field of autonomous driving which has been studied considerably less than urban driving. To further research in this area, we implement a set of extensions spanning reinforcement learning (RL), Computer Vision (CV), and robotics interfaces upon the Learn-to-Race framework, which itself runs on top of a racing simulator. Our project also has a software development component that involves creating interfaces to connect to an actual vehicle using ROS. These research and development thrusts are crucial to designing safe and fast autonomous agents, as failures in real-life are exceptionally costly. The safe policies learned by the autonomous racers can be generalized to the real world to have safer and faster autonomous driving agents. |
EnvPool
Yukun Jiang, Leo Guo, Yufan Song, Ting Luo, Tianyi Sun, Peilin Rao, |
Multimodal Question Answering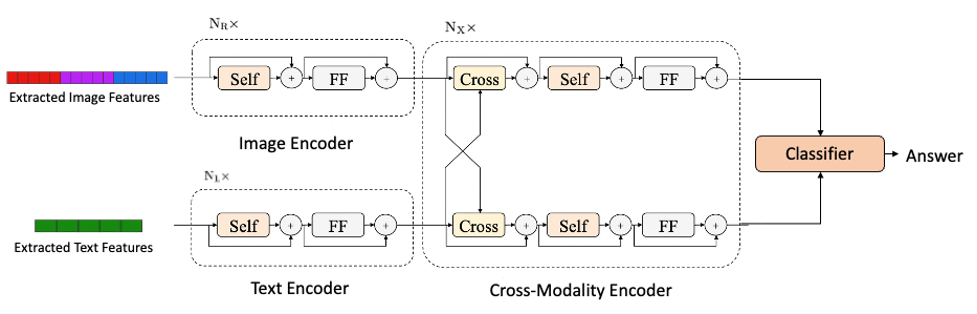
Kunal Dhawan, Manoj Ghuhan Arivazhagan, Wenxing Deng Multimodal Question Answering (MQA) is a rapidly growing area of research that aims at building intelligent systems that can respond to user queries by reasoning over information from multiple modalities. Such systems try to emulate human beings who also rely on cross-modal reasoning to answer any question thrown at them. Current MQA approaches suffer from various drawbacks like biased datasets used for training, the inability to answer simple counting-based questions, and the tendency to learn surface-level relationships rather than building reasoning. In this work, we aim to overcome these limitations and propose a new end-to-end MQA system. The major contributions of this work would be: 1) Curation of an MQA dataset which consists of a diverse set of question types capturing complex interactions and relationships between different objects in the images and is devoid of any inherent biases, 2) Improved feature extraction module which can handle and even generate scene graphs given input images, 3) Instance segmentation module to improve MQA system performance for counting related questions, 4) End-to-end trainable MQA pipeline which outperforms the current state-of-the-art. |
ASML YieldStar: Particle / Defect Detection and Classification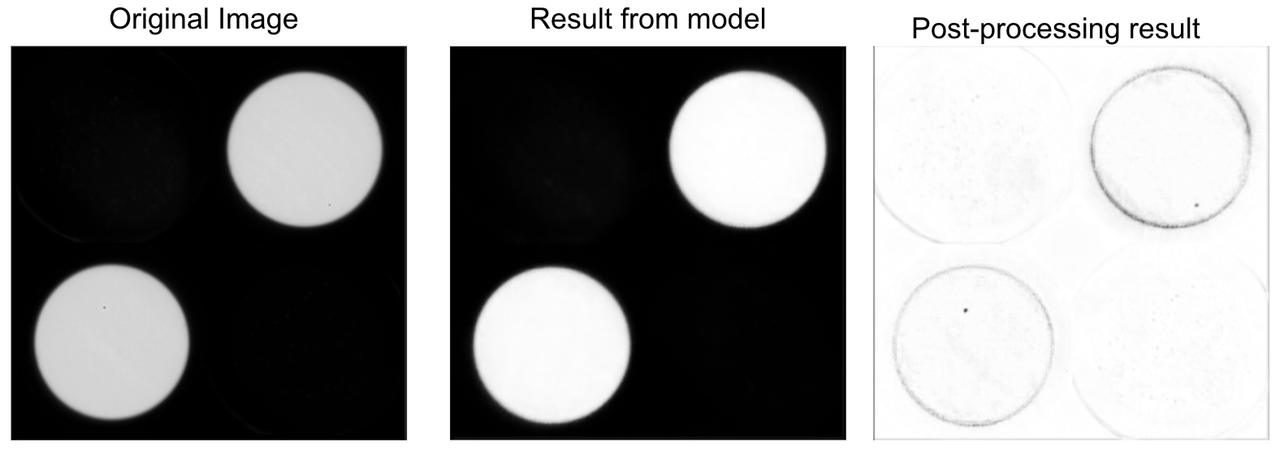
Mahalakshumi Visvanathan, Wei-Chieh Chen, Yijia Zhang YieldStar is an advanced wafer metrology technique provided by ASML. It is used to verify the quality of the produced wafer. However, even tiny errors could affect production since YieldStar has complicated and expensive optics. Currently, production technicians rely on their knowledge to catch defects. This process takes over 500 hours per year, which is very time-consuming. To improve production efficiency, we've proposed two major techniques to improve it: a classification Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), which can detect if a particle is present or not, and a Convolutional Auto-Encoder that can localize and measure the intensity of the particle. |
Predicting Flatness Error with ASML Wafer Table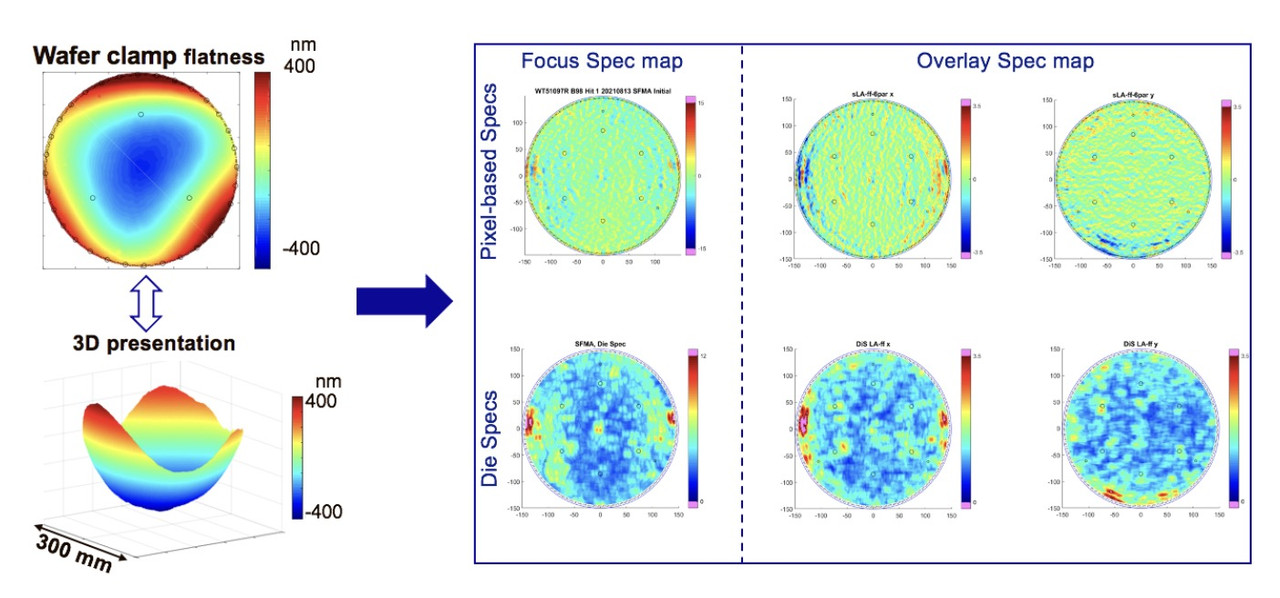
Tz-Ruei Liu, I-Tsun Cheng, Xinyan Xie At ASML, the flatness error of wafer tables is computed manually using a fixed formula. Although exact, the current system takes more than 5 minutes to compute all spec maps per sample, which is inefficient. In this work, we introduce a machine-learning method that predicts spec maps with sufficiently small errors while being substantially faster. We use U-Net and its variant SmaAt-UNet and show that they perform very effectively at our task. Equipped with attention and depthwise-separable convolutions, SmaAt-UNet achieves less than 2% error across all spec maps while taking only 30 seconds to compute, 10x faster than the current system. |
Self Driving Databases Management System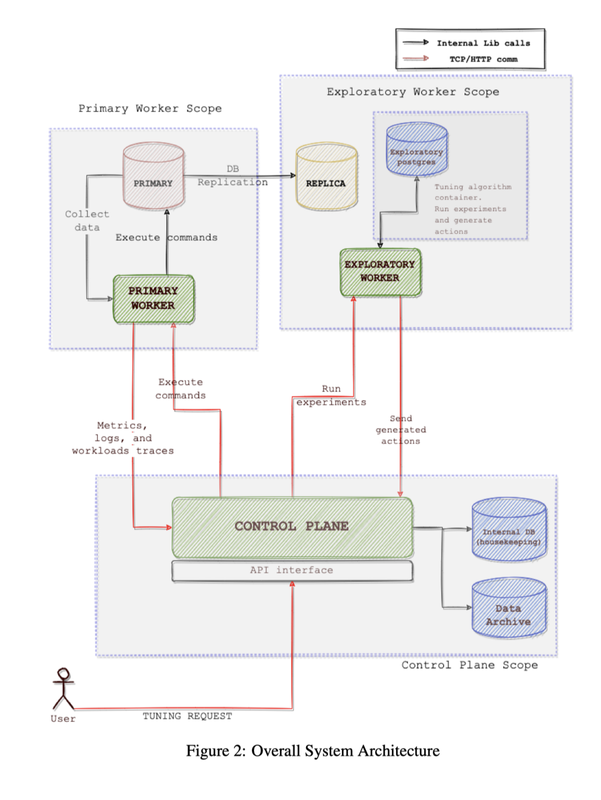
Kushagra Singh, Lichen Jin, He-Wei Lee Our project presents the control plane for self-driving database systems -- a framework that orchestrates database tuning operations and manages resources for production database clusters hosted in heterogeneous environments. |
Autobatch - Ragged Tensor's Shape Representation and Efficient Computation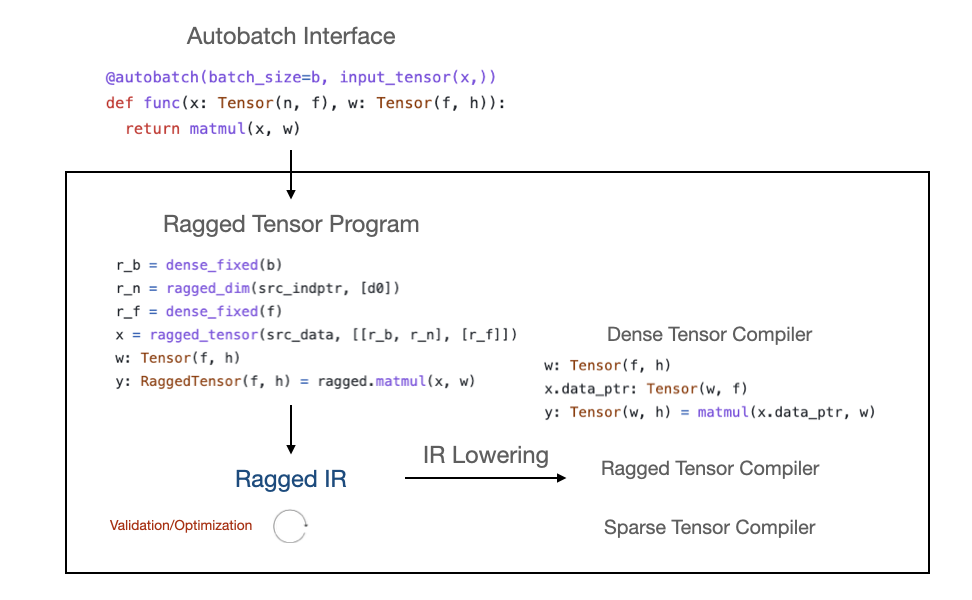
Bowen Chen In this report, we will introduce a new shape representation of the Ragged Tensor, which is a typical input workload in NLP models. We will discuss: the design of Ragged Tensor Intermediate Representation (IR), the implementation of Ragged Tensor API upon Relax, a graph level optimization based on RaggedTensor IR, and an auto-batch user interface enabled by Ragged Tensor IR. |
Secure NLP Inference
Shreya Sharma With the advent of cloud computing benefits such as elasticity and availability at affordable rates, a large number of machine learning workloads are migrating to the cloud for operations. However, in this paradigm, sensitive data may be leaked to service providers if they are curious or compromised. This project aims at making existing NLP models oblivious, i.e., enabling secure inference on a trained BERT model without revealing any information about the client input data. Such a service can find uses in audits or private contract reviews, and entity recognition. |
Data Augmentation for Information Retrieval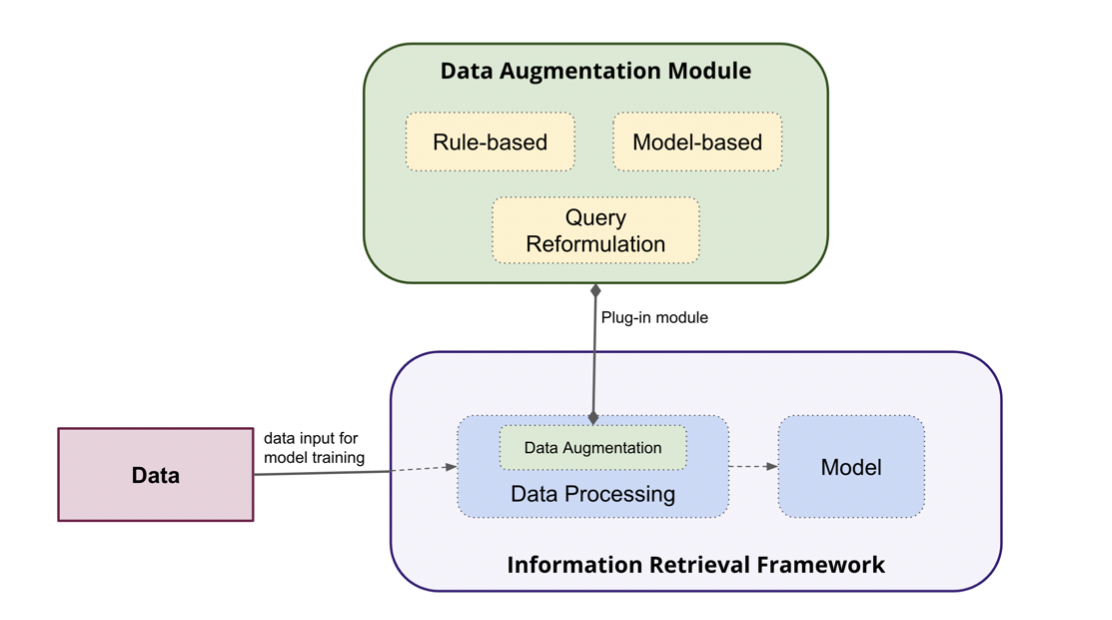
Preksha Patel, Ramya Ramanathan, Riddhi Nisar, Sayani Kundu, Vivek Sourabh In our capstone, we aim to build a data augmentation module, which can be easily plugged into the pipeline of Information Retrieval frameworks. We also aim to finetune and improve the re-ranker in FlexNeuART using augmented data. We use the MS MARCO passage re-ranking dataset for this task and implement three categories of data augmentation techniques - rule-based, model-based, and query reformulation. We evaluate our results on the mean reciprocal rank (MRR) metric. |
Simbot Dialog and Language Generation
Shubham Phal, Nikhil Gupta, Prasoon Varshney, Shubham Virmani, Benny Jiang, Xinyue Chen Our work on the Simbot Challenge asks a basic question: How does language change when situated? How do objects in the environment and behaviors of people around us inform how language utterances are interpreted? Our project uses advanced NLP techniques to model a two-way free-form dialogue between a commander and a multimodal embodied agent to perform a plethora of complex tasks in a simulated environment. |
Programmable Storage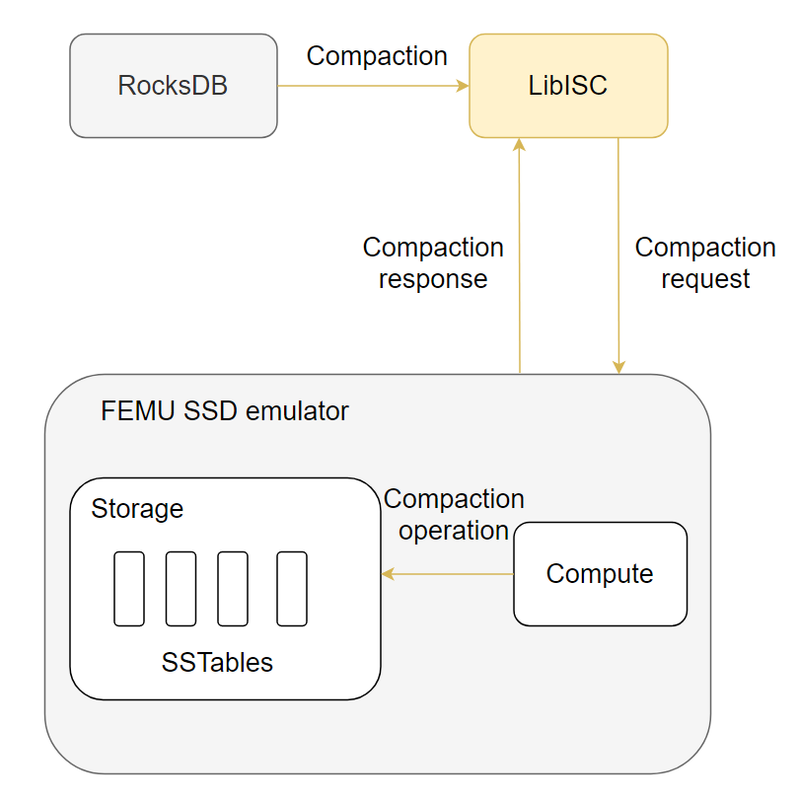
Jiuzhi Yu, Sumanth Rao With more data to analyze in this big data era, traditional CPU-centric processing is constrained by the large volume of data transferred between the storage system and memory. In the meantime, with the advances in the computational storage devices in the industry, we are seeing the potential of offloading computation to a storage device to optimize the applications which process large amounts of data.In this project, we explore the potential of offloading RocksDB compaction operations and demonstrate the performance gain for the operation itself and for the whole system. |
Automated Sensemaking for Online Tasks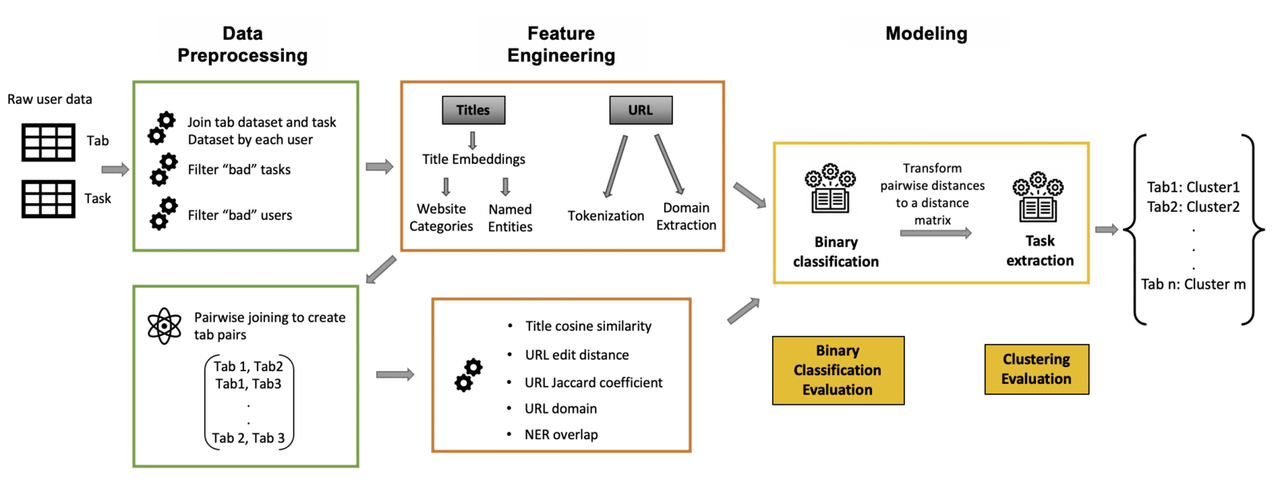
Shuyu Jiang, Ye Rin Han Skeema is an extension of the Google Chrome browser where users can manually organize their open tabs and nest them under user-defined tasks. We aim to enable Skeema to automatically categorize users' open tabs into tasks. We generate multiple features from the tab URL and title and build a Multi-layer Feed-forward Neural Network to experiment with different combinations of features. Using the distance matrix generated from the classifier, we create clusters of tabs through Agglomerative Clustering. The final clustering model achieves 0.8389 accuracy, and this result demonstrates that our approach to engineering the new features and model architecture is promising. |
Intelligent Text-Conditioned Music Generation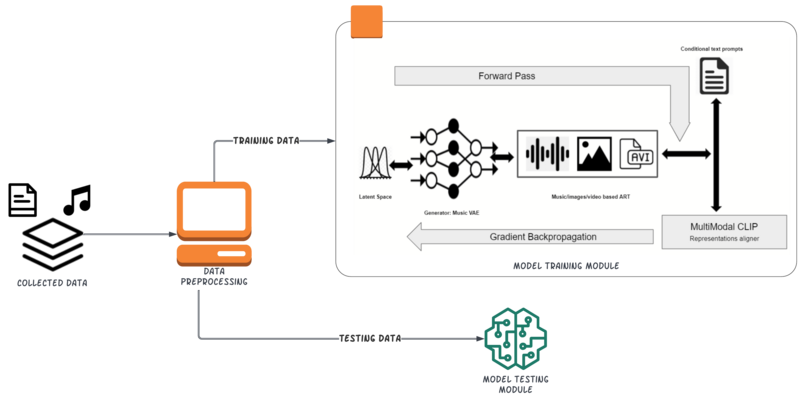
Zhouyao Xie, Nikhil Yadala, Xinyi Chen, Jingxi Liu Despite recent advancements in neural generative models and multimodal machine learning, the task of conditional music generation remains a niche research area that is largely under-explored. Inspired by CLIP, which learns to align image and text modalities through contrastive learning, we propose MusicCLIP, a text-conditioned music generation model with an encoder-decoder architecture. In the encoder part, the Transformer-based music encoder and text encoder learn to align each other through contrastive learning. In the decoder part, a music decoder generates symbolic music from latent embeddings using nucleus sampling. |
Accelerated Cloud for Artificial Intelligence - Systems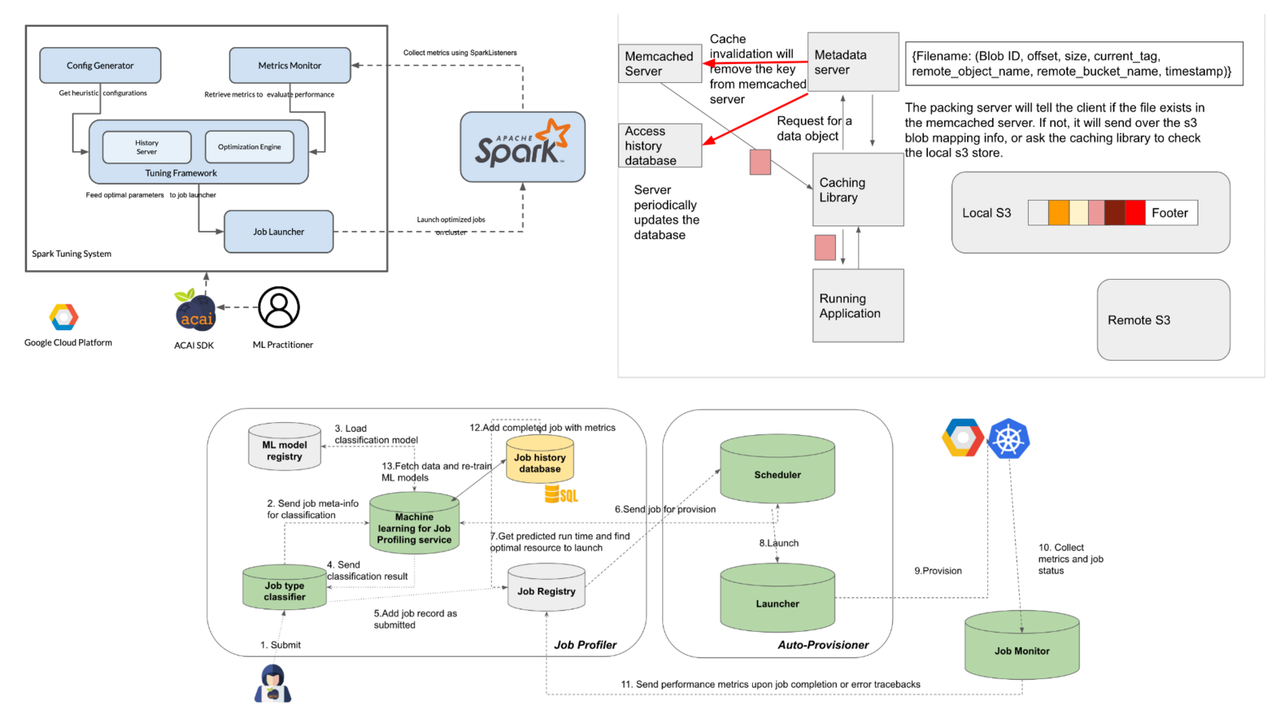
Hao Yang Lu, Eeshwar Gurushankar Prasad, Shantanu Kamath, Chenda Zhang ACAI helps ML practitioners focus on model development by providing utilities that reduce the development and deployment overheads that come with cloud infrastructure. We have implemented three novel features into the existing ACAI framework. |
Stargate: Towards DynamoDB Compatibility for Cassandra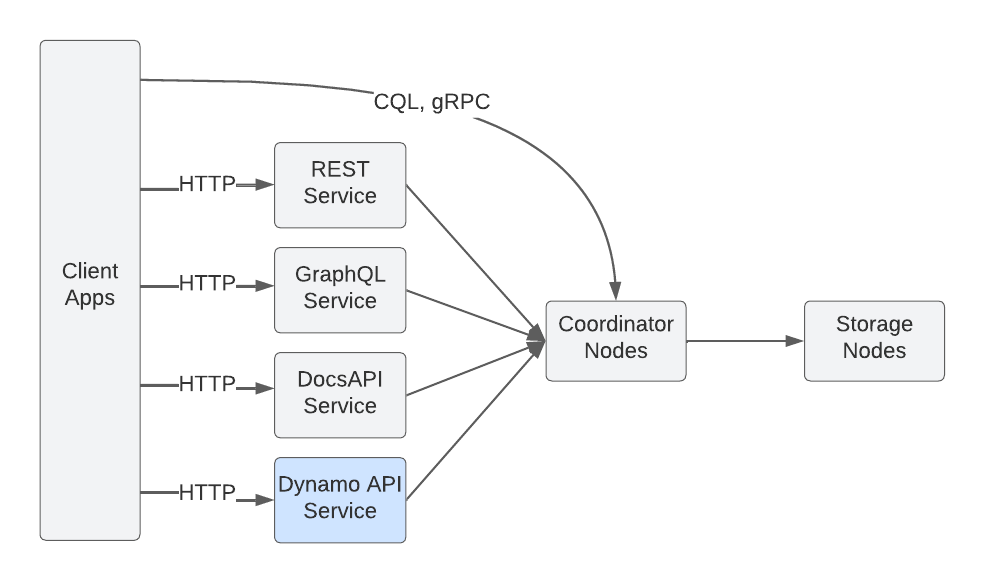
Boxuan Li, Xiang Yue, Ziyan Zhang We aim to develop a middleware that can bring DynamoDB API compatibility to Apache Cassandra so that DynamoDB applications can switch to Apache Cassandra seamlessly. |
End-to-end Model Probing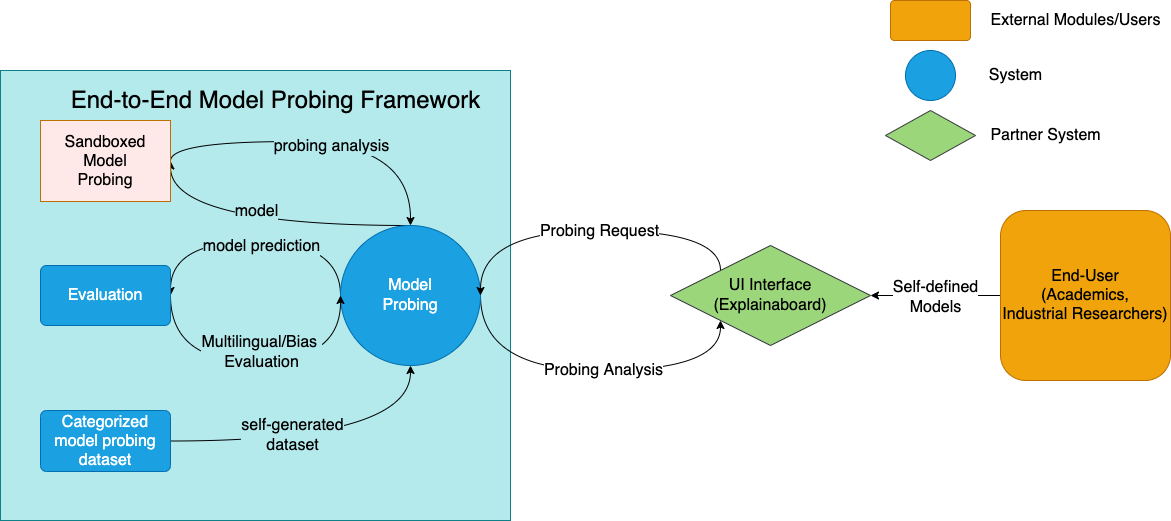
Yunxuan Xiao, Ashley Wu, Su Park, Divija Nagaraju We introduce a theoretical and empirical framework for end-to-end model probing, which probes models for their ability to capture certain linguistic phenomena. We also discovered potential correlations between complex semantic tasks and low-level tasks from the probing results. |
Data Pipeline Wind Tunnel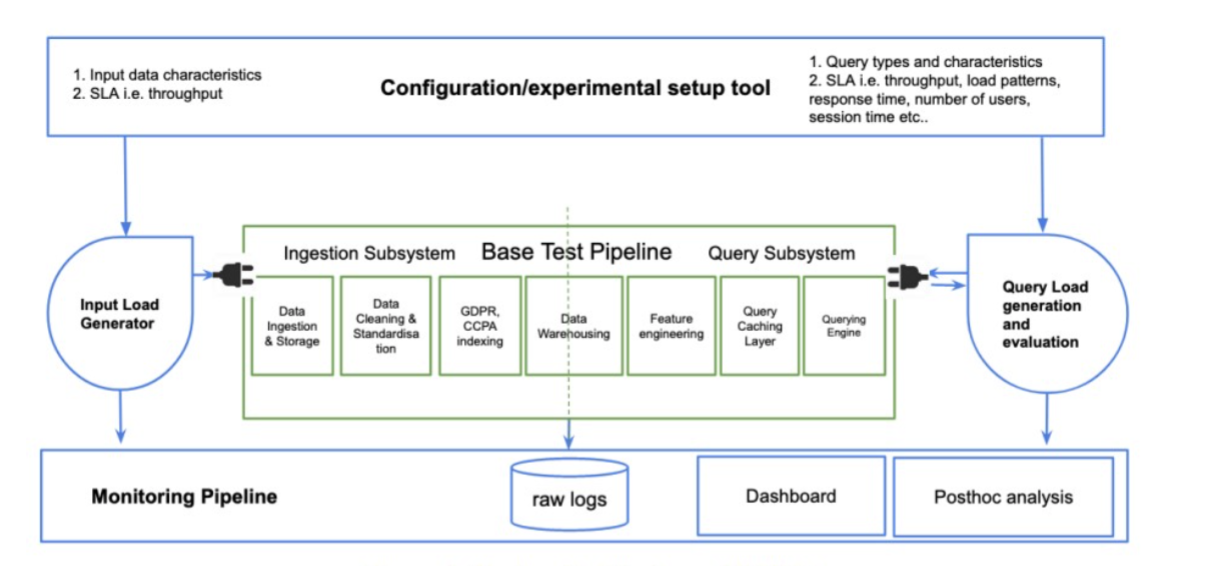
Shicheng Huang Data pipeline wind tunnel is an end-to-end benchmarking system to allow stakeholders to evaluate the pipeline performance and make iterative modifications based on different configurations. |
Accelerated Cloud for Artificial Intelligence - AutoML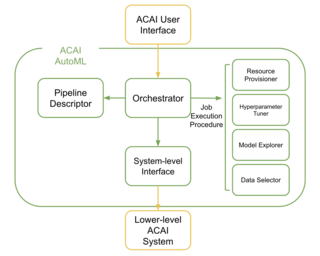
Jiyu Hu, Ruben Mampilli, Ke Sun ACAI AutoML provides a solution to machine learning tuning through automating machine learning experimentation based on a user-specified pipeline and outputting an optimal configuration for the problem. It achieves fully automatic pipeline tuning with the combined effort of model selection, data sub-sampling, and hyper-parameter tuning. In this project, new pipeline execution features are added to the existing implementation of ACAI AutoML, improving its performance in both output model performance and execution time. The comparison to auto-sklearn, a state-of-the-art AutoML platform, shows that ACAI AutoML achieves similar, if not better, pipeline tuning performance and supports a much larger variety of pipelines. |
AI Presentation Coach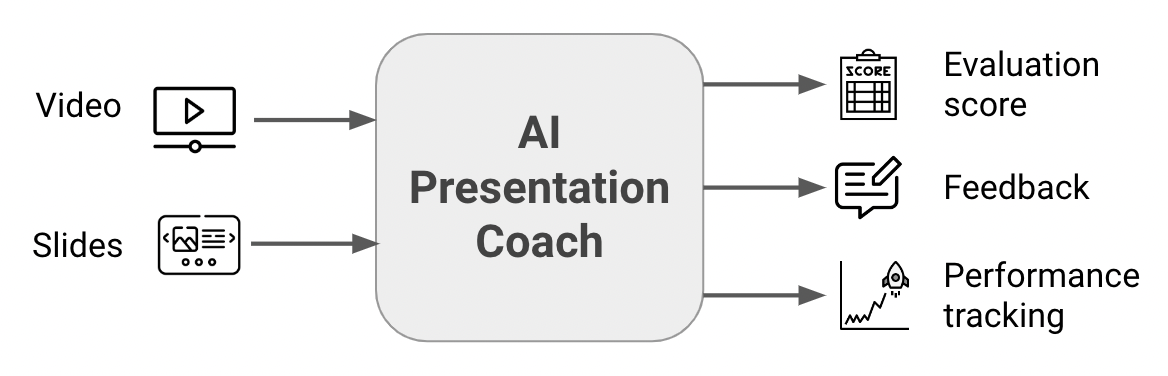
Huiyi Zhang, Venny Ayudiani Presentation is one of the most common methods to convey ideas and share information, and presentation skills can be improved by training and evaluation. AI Presentation coach is an end-to-end AI-based system that automatically evaluates the effectiveness of the presentation and provides actionable feedback for the presenters to improve their skills. AI Presentation Coach aims to extract features from each constituent of a presentation, use multimodal machine learning to evaluate the presenter's performance across different presentation aspects, and provide actionable feedback to the presenter. |
Understanding of Molecular and Evolutionary Mechanisms for Protein Temperature Adaptation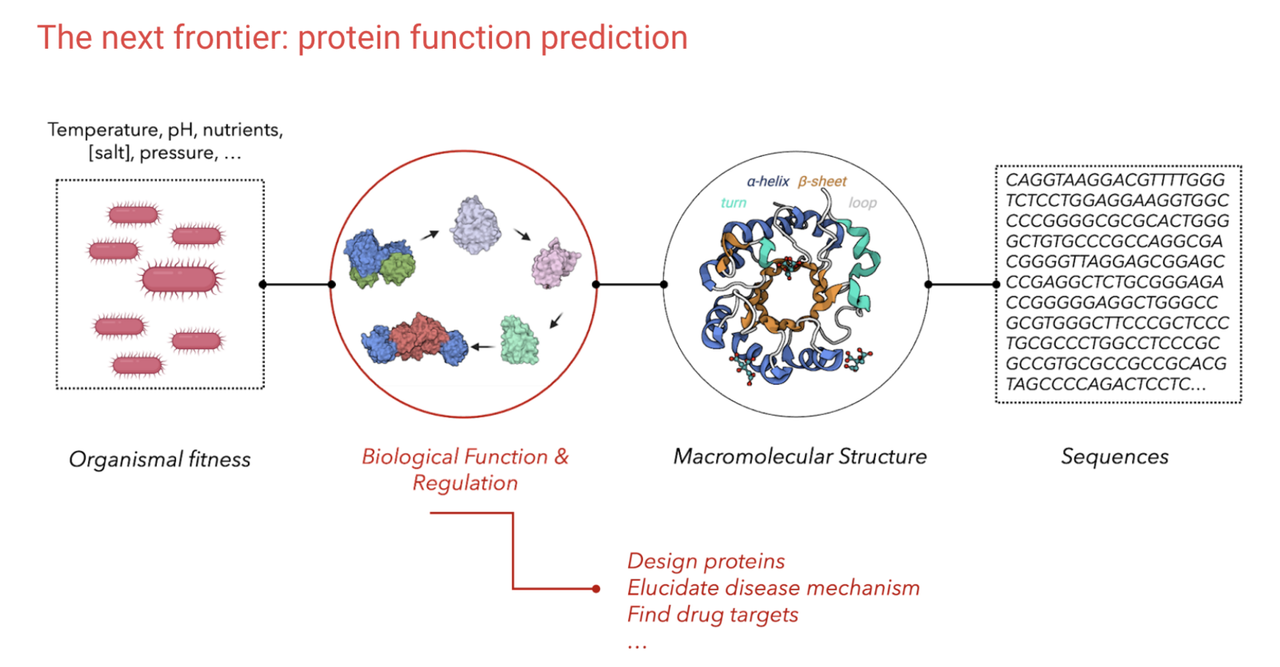
Yuting Deng Billions of years of evolution have produced millions of diverse species. Adaptation is driven by changes in molecules whose functions give rise to life. Temperature acting as the driving force for evolutionary processes decides the adaptation of protein stability and activities. To demystify the molecular mechanisms underlying protein and temperature adaptation, this project aims to investigate proteins' thermostability through computational methods. Since a well-annotated functional database of protein is lacking, we curated a large-scale well-annotated functional database across archaea and bacterias, including ~9947 ortholog groups annotated by 40 critical function labels under rigorous quality control. In the future, this dataset would be of great value in dissecting biophysical forces that drive protein evolution through identifying temperature-associated residues and trends in temperature-associated residue properties and interactions. |
Information Retrieval: NERQ (Named Entity Recognition for Queries)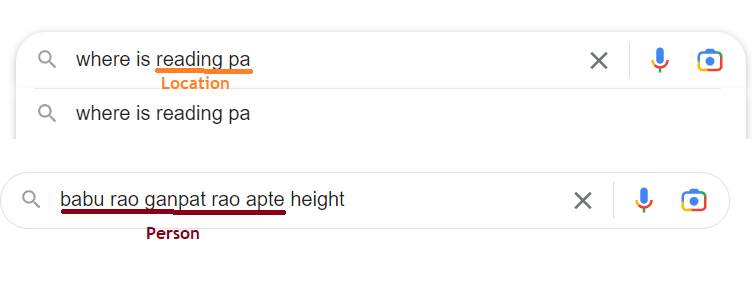
Dhruv Arya, Nidhi Dhar, Sarthak Tandon Named Entity Recognition on web search queries (NERQ) has been noted as a challenging problem in the literature. The reduction in context, irregular grammar, and lack of proper casing in queries makes it difficult for off-the-shelf NER models to perform well on queries. This paper introduces a new and challenging supervised dataset for NERQ created from the MS MARCO dataset and performs experiments to improve the performance of the current state-of-the-art models on this dataset. These models show significant performance gains in experiments that perform finetuning with domain-transferred data. |
Exploring Trust and Strategies in Agent-Human teaming
Annie Johnson This work delves into evaluating trust in agent-human teaming in the gaming domain. This capstone project combines a Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) component as well as an analytic component. Here we provide a definition of “trust” relevant to the Overcooked game and perform a study where volunteers play this game and answer survey questions based on their experience. The game-play videos recorded during the study were used to train an Object Recognition model to test the robustness of the video. Self-Organizing Maps were used to cluster the trajectories obtained from the game to identify the factors that influence trust. |
AI2F: Artificial Intelligence Integrated Fires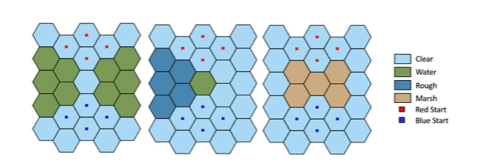
Simon Knapp, Eric Youn, Rebecca Wilson The current military planning process is slow and deliberate and requires days or even weeks of dedicated staff personnel. Our solution attempts to solve this problem for artillery planning by applying reinforcement learning to develop agents that can rapidly develop courses of action and wargame various scenarios. On a broader scale, the simulation environment we are currently developing alongside the US Army Engineer Research and Design Center (ERDC) provides researchers with a valuable tool for rapidly developing agents for other aspects of military planning. Our experiments explore the training methods for agents using this framework and how agents learn to apply indirect fires and ammunition selection in it. |
Nudge
Hermes Suen Nudge is a project aimed at creating a platform for individuals, institutions, and organizations to invest in real-life behavior change. It is built on the assumption of memetic desire and social contagion and provides monetary rewards to creators of viral TikToks that are related to the desired behavior change. |